Diana’s Certified Certified Big Data Engineer
Overview
The Certified Big Data Engineer course is designed to provide individuals with the skills and knowledge necessary to excel in the field of big data engineering. This certification program typically covers a range of topics related to big data technologies, data processing, and data infrastructure. While the specific details of the course may vary depending on the organization offering it, here is a general overview of what a Certified Big Data Engineer course entails:
1. Purpose: The course aims to equip individuals with the skills required to design, build, and maintain large-scale data processing systems. It focuses on the technical aspects of big data engineering, including data storage, data processing frameworks, data pipelines, and infrastructure management.
2. Key Concepts: The course covers key concepts related to big data engineering, such as distributed systems, data scalability, fault tolerance, data partitioning, and data integration.
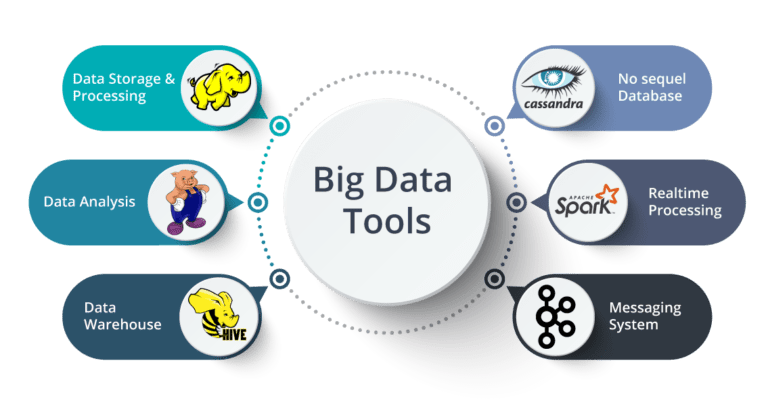
3. Big Data Technologies: Participants are introduced to various big data technologies and frameworks commonly used in the industry. This may include Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Kafka, Apache Hive, Apache HBase, and other related tools.
4. Data Processing and Analysis: The course explores techniques and best practices for processing and analyzing large volumes of data. Participants learn how to design and implement efficient data processing workflows, perform batch and real-time data processing, and apply data analytics algorithms.
5. Data Storage and Management: The course covers different data storage solutions suitable for big data, including distributed file systems (e.g., Hadoop Distributed File System – HDFS), NoSQL databases (e.g., Cassandra, MongoDB), and columnar databases (e.g., Apache Parquet).
6. Data Integration and ETL: Participants learn about data integration techniques, including Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes, and data ingestion from various sources. They gain knowledge of tools and frameworks for data integration and data pipeline orchestration.
7. Scalability and Performance Optimization: The course emphasizes strategies for scaling big data systems and optimizing performance. Participants learn about techniques for horizontal scaling, data partitioning, data replication, and query optimization.
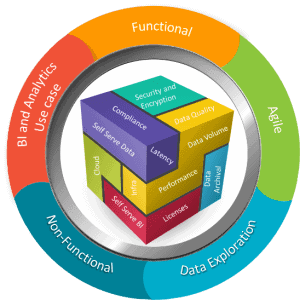
8. Data Governance and Security: The course addresses data governance principles and security considerations specific to big data engineering. Participants learn about data privacy, access control, data encryption, and compliance with data protection regulations.
9. Infrastructure Management: Participants gain knowledge of infrastructure management practices for big data environments. This may include concepts related to cloud computing, containerization (e.g., Docker, Kubernetes), and cluster management.
10. Real-world Applications: The course may include case studies and practical exercises that simulate real-world big data engineering scenarios. Participants have the opportunity to apply their knowledge and skills to solve practical problems and work with big data technologies in hands-on projects.
Prerequisites
The prerequisites for the Certified Big Data Engineer course can vary depending on the organization or institution offering the certification program. However, here are some common prerequisites that are often recommended or required for candidates pursuing a Big Data Engineer certification:
1. Technical Background: A strong technical background in computer science, software engineering, or a related field is typically recommended. Candidates should have a solid understanding of programming concepts, data structures, algorithms, and computer architecture.
2. Programming Skills: Proficiency in programming languages commonly used in big data engineering is essential. Candidates should have experience with languages such as Java, Python, Scala, or SQL. They should be comfortable writing code and working with data manipulation, processing, and analysis.
3. Database and SQL Knowledge: Familiarity with databases and SQL (Structured Query Language) is important. Candidates should have a good understanding of relational databases, data modeling, and SQL queries to effectively work with and manage large volumes of data.
4. Distributed Computing: Knowledge of distributed computing concepts and frameworks is crucial for big data engineering. Candidates should have an understanding of distributed systems, parallel processing, and concepts like MapReduce and data partitioning.
5. Data Processing and Analysis: Familiarity with data processing and analysis techniques is beneficial. Candidates should have knowledge of concepts like batch processing, real-time streaming, data analytics, and data transformation.
6. Hadoop Ecosystem: Understanding the Hadoop ecosystem, including Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, and related tools and technologies, is often required. Candidates should be familiar with the fundamentals of Hadoop, its architecture, and the components of the ecosystem.
7. Linux and Command Line: Proficiency in using the Linux operating system and command line interfaces is recommended. Candidates should have basic knowledge of shell scripting, file management, and system administration tasks.
8. Data Warehousing and ETL: Familiarity with data warehousing concepts and Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes is valuable. Candidates should understand data integration, data quality, and data governance principles.
9. Cloud Computing: Knowledge of cloud computing platforms, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP), is beneficial. Candidates should have a basic understanding of cloud-based infrastructure and services for big data processing and storage.
Audience
The Certified Big Data Engineer course is typically aimed at individuals who are interested in developing their skills and expertise in the field of big data engineering. The course is designed to cater to a diverse audience with varying levels of experience and backgrounds. Here are some potential target audiences for the Certified Big Data Engineer course:
1. IT Professionals: Professionals already working in the IT industry, such as software engineers, data engineers, database administrators, or system administrators, can benefit from the Certified Big Data Engineer course. It allows them to specialize in big data technologies and acquire the skills needed to design and manage large-scale data processing systems.
2. Data Professionals: Data professionals, including data analysts or data scientists, who want to expand their skill set and move into a role focused on big data engineering can benefit from this course. It provides them with the knowledge and tools to handle large volumes of data, design efficient data processing pipelines, and work with big data frameworks.
3. Software Developers: Software developers looking to enhance their skills in the area of big data engineering can take the course to learn about the tools and technologies used in the field. This enables them to work on projects involving big data processing, data integration, and distributed systems.
4. Graduates and Students: Recent graduates or students pursuing degrees in computer science, software engineering, or related fields can take the course to gain expertise in big data engineering. It can improve their employability and open up opportunities in industries that deal with large-scale data processing.
5. Technology Managers: Managers and team leads who are responsible for overseeing big data projects can benefit from the course to understand the technical aspects of big data engineering. This allows them to effectively communicate with their team, make informed decisions, and ensure the successful implementation of big data solutions.
6. Business Analysts: Business analysts seeking to gain a deeper understanding of big data engineering can enroll in the course. It equips them with the knowledge to work with large datasets, analyze data, and extract meaningful insights that can drive business decisions.
7. Data Architects: Data architects who want to specialize in big data architecture and design can benefit from the Certified Big Data Engineer course. It provides them with the necessary skills to design scalable and efficient data processing systems using big data technologies.
8. Data Science Enthusiasts: Individuals with a keen interest in big data and data science can take the course to gain a solid foundation in big data engineering. It allows them to understand the technical aspects of working with large datasets and apply data engineering principles to support data-driven decision-making.
Skillset
To excel in the Certified Big Data Engineer course and work effectively in the field of big data engineering, participants are expected to develop a specific skill set. While the exact skill requirements may vary depending on the course curriculum and the organization offering the certification, here are some common skills that are often emphasized in a Certified Big Data Engineer program:
1. Big Data Technologies: Familiarity with big data technologies and frameworks is essential. This includes Apache Hadoop and its ecosystem (HDFS, MapReduce, Hive, Pig, etc.), Apache Spark, Apache Kafka, Apache HBase, and other relevant tools. Participants should understand the purpose, features, and usage of these technologies.
2. Programming Skills: Proficiency in programming languages commonly used in big data engineering is necessary. Candidates should have experience with languages such as Java, Python, Scala, or SQL. They should be able to write code, manipulate data, and work with big data frameworks and libraries.
3. Distributed Computing: Knowledge of distributed computing concepts and frameworks is crucial. Participants should understand parallel processing, data partitioning, fault tolerance, and scalability in distributed systems. Familiarity with frameworks like Apache Spark for distributed data processing is important.
4. Data Processing and Analysis: Participants should have a solid understanding of data processing and analysis techniques. This includes batch processing, real-time streaming, data transformation, data cleansing, and data aggregation. They should be able to implement data processing workflows and apply analytics algorithms.
5. Data Storage and Management: Familiarity with various data storage solutions is important. Candidates should understand distributed file systems (such as Hadoop Distributed File System – HDFS), NoSQL databases (like Cassandra or MongoDB), columnar databases, and data warehousing concepts. Knowledge of data modeling and database design is beneficial.
6. Data Integration and ETL: Participants should have knowledge of data integration techniques and Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes. This includes data ingestion from multiple sources, data transformation, data quality, and data integration best practices. Understanding tools and frameworks for data integration is valuable.
7. Cloud Computing: Familiarity with cloud computing platforms, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP), is valuable as big data engineering often leverages cloud-based infrastructure. Knowledge of provisioning resources, managing clusters, and deploying big data applications in the cloud is beneficial.
8. Data Governance and Security: Understanding data governance principles and data security considerations is important. Participants should be aware of data privacy regulations, access control mechanisms, data encryption, and data governance frameworks.
9. Troubleshooting and Optimization: Participants should be able to troubleshoot issues related to big data systems and optimize their performance. This includes diagnosing and resolving data processing bottlenecks, optimizing queries, and identifying performance improvement opportunities.
10. Communication and Collaboration: Effective communication skills are crucial for collaborating with team members and stakeholders. Participants should be able to clearly communicate complex technical concepts and work effectively in a team-based environment.